What Specific Ways Can a Session Token Be Transmitted?
This post volition explore the concept of refresh tokens as defined by OAuth ii.0. We will learn how they compare to other token types and how they let us balance security, usability, and privacy.
What Is A Token?
Tokens are pieces of data that carry only plenty information to facilitate the process of determining a user'south identity or authorizing a user to perform an action. All in all, tokens are artifacts that allow application systems to perform the authorization and authentication process.
New to identity concepts? Read Authentication vs Authorization to get started.
Common identity frameworks and protocols use token-based strategies to secure admission to applications and resources. For example, nosotros tin can utilise OAuth two.0 for authorization and OIDC for authentication.
OAuth 2.0 is one of the nearly popular authorization frameworks out there. It is designed to allow an awarding to access resources hosted by other servers on behalf of a user. OAuth two.0 uses Access Tokens and Refresh Tokens.
OpenID Connect (OIDC) is an identity protocol that performs user authentication, user consent, and token issuance. OIDC uses ID Tokens.

Let's explore the three token types that nosotros use with OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect to fulfill the authentication and authorization processes of our application systems. In the process, we'll see the critical role that refresh tokens play in helping developers build applications that offer convenience without compromising security.
Token Types
What'due south an ID token?
As the name may suggest, an ID token is an artifact that client applications tin apply to swallow the identity of a user. For case, the ID token can contain information about the proper noun, email, and profile picture show of a user. As such, customer applications can use the ID token to build a user profile to personalize the user experience.
An authentication server that conforms to the OpenID Connect (OIDC) protocol to implement the hallmark procedure issues its clients an ID token whenever a user logs in. The consumers of ID tokens are mainly client applications such as Single-Page Applications (SPAs) and mobile applications. They are the intended audience.
What'south an access token?
When a user logins in, the authorization server issues an access token, which is an antiquity that customer applications can use to make secure calls to an API server. When a client application needs to access protected resource on a server on behalf of a user, the access token lets the customer signal to the server that information technology has received authorisation by the user to perform sure tasks or access certain resources.
OAuth ii.0 doesn't ascertain a format for access tokens. At Auth0, for example, admission tokens issued for the Management API and access tokens issued for whatsoever custom API that you lot have registered with Auth0 follow the JSON Web Token (JWT) standard. Their basic construction conforms to the typical JWT structure, and they incorporate standard JWT claims asserted about the token itself.

This is the content of a decoded access token that follows the JWT format:
{ "iss" : "https://YOUR_DOMAIN/" , "sub" : "auth0|123456" , "aud" : [ "my-api-identifier" , "https://YOUR_DOMAIN/userinfo" ] , "azp" : "YOUR_CLIENT_ID" , "exp" : 1489179954 , "iat" : 1489143954 , "scope" : "openid contour email address phone read:appointments" } It's important to highlight that the access token is a bearer token. Those who concord the token can use it. The access token then acts as a credential artifact to access protected resources rather than an identification artifact. Malicious users could theoretically compromise a system and steal access tokens, which in turn they could apply to access protected resource by presenting those tokens directly to the server.
Every bit such, it'south critical to have security strategies that minimize the hazard of compromising admission tokens. I mitigation method is to create access tokens that have a brusque lifespan: they are simply valid for a short time defined in terms of hours or days.
In that location are different ways that a customer application can get a new admission token for a user. For example, once an access token expires, the client application could prompt the user to log in again to get a new access token. Alternatively, the authorization server could issue a refresh token to the client application that lets it replace an expired access token with a new one.
Yous tin run into both ID tokens and access tokens in action in whatever of our "Complete Guides to User Authentication" available for React, Angular, Vue, and Node.js!
What Is a Refresh Token?
As mentioned, for security purposes, access tokens may exist valid for a curt amount of time. In one case they expire, client applications tin can use a refresh token to "refresh" the admission token. That is, a refresh token is a credential artifact that lets a client application get new access tokens without having to ask the user to log in once again.
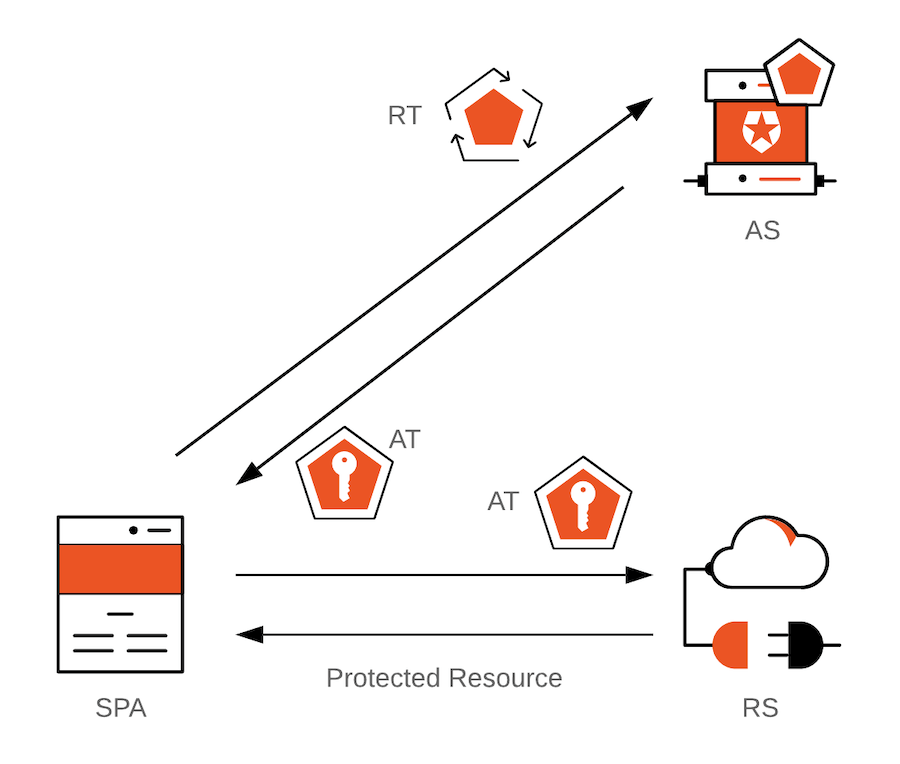
In the diagram higher up, SPA = Single-Page Application; Equally = Potency Server; RS = Resource Server; AT = Access Token; RT = Refresh Token.
The customer application can go a new admission token every bit long every bit the refresh token is valid and unexpired. Consequently, a refresh token that has a very long lifespan could theoretically give infinite ability to the token bearer to get a new access token to access protected resources someday. The bearer of the refresh token could be a legitimate user or a malicious user. As such, security companies, such as Auth0, create mechanisms to ensure that this powerful token is mainly held and used continuously by the intended parties.
When to Use Refresh Tokens
Information technology'due south important to keep in mind that the OAuth 2.0 specification defines access tokens and refresh tokens. So, if we were to discuss authorization strategies in terms of other identity protocols or frameworks, such as SAML, we would non have the concepts of access tokens or refresh tokens.
For those involved with spider web evolution, access token and refresh tokens are mutual talk considering the spider web extensively uses token-based authorization and authentication through the OAuth ii.0 framework and the OpenID Connect protocol.
When combined, OAuth two.0 and OIDC bring to life an array of authorization and hallmark flows. Each flow has its ain set of benefits and caveats that define the best scenarios and compages where we should use access and refresh tokens.
-
Is the client a traditional web application executing on the server? Use the Authority Code Flow.
-
Is the client a Unmarried-Page Application (SPA)? Use Authorization Code Menses with Proof Key for Lawmaking Exchange (PKCE).
-
Is the customer a Unmarried-Page Application (SPA) that doesn't need an access token? Use the Implicit Flow with Course Mail service.
-
Is the client the resource owner? You may apply the Client Credentials Flow.
-
Is the client absolutely trusted with user credentials? You may use the Resources Owner Password Flow.
If there'southward an app for that, there'south too a menses for that!
Keep in heed that co-ordinate to the spec, when using the Implicit Flow, the authority server should not consequence refresh tokens. The Implicit menstruation is often implemented in Single-Folio Applications (SPAs), which run on the frontend layer of a organization architecture. There's no easy way of keeping a refresh token secure in the frontend layer on its own.
Using the Authorization Code Flow with Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) mitigates many risks inherent to the Implicit Catamenia. For example, when using the implicit grant blazon, the access token is transmitted in the URI fragment, which can betrayal it to unauthorized parties. You can learn more nearly these vulnerabilities past reading the "Misuse of Admission Token to Impersonate Resource Owner in Implicit Flow" section of the spec.
However, implementing PKCE in your applications withal has no impact on how secure refresh tokens are.
However, you may not need refresh tokens.
There are scenarios where you can still go an admission token without interrupting the user and without relying on the almighty power of the refresh token. Other examples to keep a session going can be cookies or silent authentication.
However, billions of people use SPAs every day. It is important to provide users with a user experience that balances security and convenience well. Is there anything that we could do to let SPAs afford the convenience of refresh tokens in a less risky and more secure fashion?
Absolutely!
An identity platform that offers Refresh Token Rotation makes it acceptable to use refresh tokens with Unmarried-Page Applications. The spec underlines that when y'all can not verify that a refresh token belongs to a client, such a SPA, nosotros should non use them unless we have Refresh Token Rotation in place.
Let's learn more than about this security strategy in the adjacent section.
Keeping Refresh Tokens Secure
A brusk-lived access token helps improve the security of our applications, but it comes with a price: when it expires, the user needs to log in once again to go a new one. Frequent re-hallmark can diminish the perceived user feel of your application. Fifty-fifty if you are doing then to protect their information, users may detect your service frustrating or difficult to use.
A refresh token can help you residual security with usability. Since refresh tokens are typically longer-lived, you tin can use them to asking new access tokens after the shorter-lived admission tokens expire.
However, since refresh tokens are also bearer tokens, we demand to have a strategy in place that limits or curtails their usage if they ever become leaked or become compromised. All those who hold the refresh tokens take the power to get new access tokens whenever they desire. "They" could be legitimate users or attackers.
At Auth0, we created a set of features that mitigate the risks associated with using refresh tokens by imposing safeguards and controls on their lifecycle. Our identity platform offers refresh token rotation, which besides comes with automatic reuse detection.
Allow's swoop deeper into this security technique.
Refresh Token Rotation
Until very recently, a robust strategy to help SPAs maintain the user's session was using the Authorization Code Menstruum with PKCE in conjunction with silent authentication. Refresh token rotation is a technique for getting new access tokens using refresh tokens that goes beyond silent authentication.
Refresh token rotation guarantees that every time an application exchanges a refresh token to go a new access token, a new refresh token is also returned. Therefore, you no longer accept a long-lived refresh token that could provide illegitimate access to resources if it e'er becomes compromised. The threat of illegitimate access is reduced as refresh tokens are continually exchanged and invalidated.
For example, with refresh token rotation enabled in the Auth0 Dashboard, every time your application exchanges a refresh token to get a new admission token, the authorization server too returns a new refresh-access token pair. This safeguard helps your app mitigate replay attacks resulting from compromised tokens.
Refresh Token Automatic Reuse Detection
Refresh tokens are bearer tokens. It's impossible for the potency server to know who is legitimate or malicious when receiving a new access token asking. We could so care for all users as potentially malicious.
How could we handle a situation where at that place is a race condition between a legitimate user and a malicious one? For example:
-
🐱 Legitimate User has 🔄 Refresh Token 1 and 🔑 Access Token 1.
-
😈 Malicious User manages to steal 🔄 Refresh Token 1 from 🐱 Legitimate User.
-
🐱 Legitimate User uses 🔄 Refresh Token ane to get a new refresh-access token pair.
-
The 🚓 Auth0 Authorization Server returns 🔄 Refresh Token 2 and 🔑 Access Token two to 🐱 Legitimate User.
-
😈 Malicious User then attempts to employ 🔄 Refresh Token 1 to become a new admission token. Pure evil!
What do you think should happen next? Would 😈 Malicious User manage to go a new admission token?
This is what happens when your identity platform has 🤖 Automated Reuse Detection:
-
The 🚓 Auth0 Dominance Server has been keeping track of all the refresh tokens descending from the original refresh token. That is, information technology has created a "token family".
-
The 🚓 Auth0 Dominance Server recognizes that someone is reusing 🔄 Refresh Token 1 and immediately invalidates the refresh token family, including 🔄 Refresh Token 2.
-
The 🚓 Auth0 Authorization Server returns an Access Denied response to 😈 Malicious User.
-
🔑 Access Token two expires, and 🐱 Legitimate User attempts to utilise 🔄 Refresh Token 2 to request a new refresh-access token pair.
-
The 🚓 Auth0 Authorisation Server returns an Access Denied response to 🐱 Legitimate User.
-
The 🚓 Auth0 Authorization Server requires re-hallmark to get new access and refresh tokens.
It's disquisitional for the most recently-issued refresh token to become immediately invalidated when a previously-used refresh token is sent to the authorization server. This prevents any refresh tokens in the same token family unit from being used to go new access tokens.
This protection mechanism works regardless of whether the legitimate or malicious user is able to exchange 🔄 Refresh Token 1 for a new refresh-admission token pair before the other. Without enforcing sender-constraint, the authorisation server can't know which actor is legitimate or malicious in the upshot of a replay set on.
Automatic reuse detection is a key component of a refresh token rotation strategy. The server has already invalidated the refresh token that has already been used. All the same, since the authorisation server has no way of knowing if the legitimate user is belongings the most current refresh token, it invalidates the whole token family but to be safe.
Privacy is a hot topic in our digital world. We non only need to balance security with convenience, but we also need to add privacy to the balancing act.
Recent developments in browser privacy engineering, such as Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP), prevent access to the session cookie, requiring users to reauthenticate.
In that location is no persistent storage mechanism in a browser that tin can assure access by the intended awarding just. Every bit such, long-lived refresh tokens are not suitable for SPAs as there are vulnerabilities that malicious users could exploit to obtain these loftier-value artifacts, granting them access to protected resources.
Because refresh token rotation does not rely on admission to the Auth0 session cookie, it is non affected past ITP or similar mechanisms.
Nevertheless, a refresh token could have its lifespan express by the lifespan of an access token. This means we can safely use refresh tokens to play forth with browser privacy tools and provide continuous access to stop-users without disrupting the user experience.
You Can Shop Refresh Token In Local Storage
Yes, y'all read that right. When we have refresh token rotation in place, nosotros tin can store tokens in local storage or browser retentivity.
You lot may have heard before (maybe from u.s.a.) that we should not store tokens in local storage.
Storing tokens in browser local storage provides persistence beyond page refreshes and browser tabs; nevertheless, if malicious users managed to run JavaScript in the SPA using a cross-site scripting (XSS) attack, they could retrieve the tokens stored in local storage. A vulnerability leading to a successful XSS assail could be present in the SPA source code or whatever third-political party JavaScript lawmaking the app consumes, such as Bootstrap or Google Analytics.
However, we tin reduce the absolute token expiration time of tokens to reduce the security risks of storing tokens in local storage. This reduces the bear upon of a reflected XSS assail (merely not of a persistent 1). A refresh token may have a long lifespan past configuration. Even so, the divers long lifespan of a refresh token is cut short with refresh token rotation. The refresh is only valid within the lifespan of the admission token, which would be short-lived.
Apply Refresh Tokens in Your Auth0 Apps
If you're interested in calculation authentication and authorization to your awarding in merely a few steps, sign up for a free Auth0 account now.
Try out the most powerful authentication platform for free.Get started →
Our "Token All-time Practices" document outlines some basic considerations to keep in mind when using tokens:
- Proceed information technology secret. Keep it condom.
- Do not add sensitive data to the payload.
- Give tokens an expiration.
- Cover HTTPS.
- Consider all of your authorization use cases.
- Store and reuse.
The Auth0 Dashboard makes information technology piece of cake to configure your authentication and authorization services to employ refresh tokens. Auth0 SDKs and libraries back up refresh tokens for web applications, Unmarried-Folio Applications (SPAs), and native/mobile apps.
For additional resources on how to utilise refresh tokens with Auth0, please visit any of these documents:
- Get Refresh Tokens
- Use Refresh Tokens
- Revoke Refresh Tokens
- Refresh Token Rotation
- Configure Refresh Token Expiration
Source: https://auth0.com/blog/refresh-tokens-what-are-they-and-when-to-use-them/
0 Response to "What Specific Ways Can a Session Token Be Transmitted?"
إرسال تعليق